The National Climatic Data Center reported that the intensity of this year's drought continued to worsen in August where 39.0 percent of the U.S. was in severe to extreme drought. This drought became the largest area of severe drought since December 1956 when 43.2 percent of the U.S. was in extreme drought. This year's drought is the fourth largest drought since 1895 and had a large impact on the U.S. agriculture. The U.S. Department of Agriculture reported that 52 percent of the nation's corn crop was rated poor to very poor by August 26. Soybean and sorghum also worsened and 59 percent of pasture and range land around the U.S. was very poor as well. 83 percent of corn, 80 percent of soybeans, and 72 percent of cattle were in a drought zone, you can imagine what kind of impact this had on farmers and their income.
Droughts develop slowly and can have a prolonged existence, possibly for several years and can affect all countries around the world. Human impact varies between countries depending on LDCs or MDCs. In LDCs, the drought affects the population directly where they depend on crop growth and food supplies. Low rainfall that affects the crops in these countries can lead to famine and possibly death. There is a need for better agricultural land-use practices because overgrazing, poor cropping methods, deforestation, and improper soil conservation techniques does not cause drought, but may amplify a drought disaster. Irrigation systems can offer some security against drought, but they are pricey and many farmers cannot afford such equipment. Greater diversity of cropping patterns may decrease drought risk and also water shortages. Drought forecasts that are available months ahead of time can aid the farmers in planning their crop planting and water management. This can be done by using meteorological models that look at the atmosphere and the oceans to predict rainfall for the season. It is not always affective but can provide some insight.
http://www.weather.com/news/drought-intensified-in-august-20120917
Thursday, September 27, 2012
Monday, September 24, 2012
30 Homes Damaged Near San Diego due to Brush Fire
A brush fire broke out Sunday afternoon southeast of San Diego and has burned about 2,000 acres and damaged 30 homes and at least 15 outbuildings in the area. Firefighters had 10 percent of the fire contained by this Monday morning, but progress is difficult due to windy conditions and about 80 homes are still threatened. No deaths or injuries have been confirmed by authorities, but people are concerned that elderly people may not have gotten out of their homes. The cause of the fire is still under investigation, meanwhile, some firefighters have contained about 40 percent of a separate fire in Riverside County, California, but as many as 200 homes remain threatened. This reminded me of the disaster game we had played in lab and how I thought I had taken all the right precautions for a wildfire and the wildfire still burned almost all the homes and buildings down. These dry, windy conditions make these fires that much more dangerous.
Brushfires or wildfires are uncontrolled fires that are fuelled by natural vegetation and when human activities occur in this natural vegetation, the number of wildfires and losses to life and property increases. Many small fires that do not seem threatening can become much more dangerous if strong winds whip up their flames and create spot fires, which seems to be the case in the San Diego fire. One option to resist this hazardous event from occurring is to have stricter fire ban legislation. The downside to this is not only is it difficult to enforce, but it can also increase the risk because the fuel supply is allowed to build up overtime. It is important to have controlled burns to burn away the existing fuel load, but it is labor intensive and can lead to uncontrollable fires. Although little is known of the effectiveness in forecasting and fire-weather warnings, it is still important to inform the public when restrictions on outdoor fires or declared or when there are total fire bans going on. Surveys can be done by using satellite images to detect when vegetation is "stressed" and this can indicate areas where wildfire outbreaks are most likely to occur. Land use planning and education are essential in hazard reduction, it is important to have a road network for fire fighting equipment to be accessible and for emergency evacuation. Local governments need to factor in wildfire hazards into the development control system especially with the severe drought that occurred this summer in much of the country.
http://usnews.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/09/24/14071234-brush-fire-destroys-damages-30-homes-near-san-diego?lite#__utma=238145375.1944660864.1346965793.1348357218.1348531171.6&__utmb=238145375.15.8.1348531532655&__utmc=238145375&__utmx=-&__utmz=238145375.1348531171.6.6.utmcsr=google|utmccn=%28organic%29|utmcmd=organic|utmctr=msnbc&__utmv=238145375.|8=Earned%20By=msnbc|us%20news=1^12=Landing%20Content=Mixed=1^13=Landing%20Hostname=www.msnbc.msn.com=1^30=Visit%20Type%20to%20Content=Earned%20to%20Mixed=1&__utmk=21571576
Brushfires or wildfires are uncontrolled fires that are fuelled by natural vegetation and when human activities occur in this natural vegetation, the number of wildfires and losses to life and property increases. Many small fires that do not seem threatening can become much more dangerous if strong winds whip up their flames and create spot fires, which seems to be the case in the San Diego fire. One option to resist this hazardous event from occurring is to have stricter fire ban legislation. The downside to this is not only is it difficult to enforce, but it can also increase the risk because the fuel supply is allowed to build up overtime. It is important to have controlled burns to burn away the existing fuel load, but it is labor intensive and can lead to uncontrollable fires. Although little is known of the effectiveness in forecasting and fire-weather warnings, it is still important to inform the public when restrictions on outdoor fires or declared or when there are total fire bans going on. Surveys can be done by using satellite images to detect when vegetation is "stressed" and this can indicate areas where wildfire outbreaks are most likely to occur. Land use planning and education are essential in hazard reduction, it is important to have a road network for fire fighting equipment to be accessible and for emergency evacuation. Local governments need to factor in wildfire hazards into the development control system especially with the severe drought that occurred this summer in much of the country.
http://usnews.nbcnews.com/_news/2012/09/24/14071234-brush-fire-destroys-damages-30-homes-near-san-diego?lite#__utma=238145375.1944660864.1346965793.1348357218.1348531171.6&__utmb=238145375.15.8.1348531532655&__utmc=238145375&__utmx=-&__utmz=238145375.1348531171.6.6.utmcsr=google|utmccn=%28organic%29|utmcmd=organic|utmctr=msnbc&__utmv=238145375.|8=Earned%20By=msnbc|us%20news=1^12=Landing%20Content=Mixed=1^13=Landing%20Hostname=www.msnbc.msn.com=1^30=Visit%20Type%20to%20Content=Earned%20to%20Mixed=1&__utmk=21571576
Wednesday, September 19, 2012
Arctic Sea Ice Sets a New Low
The Arctic Sea ice has officially stopped melting for the year according to scientists, but has also beat the previous record. According to the National Snow and Ice Data Center the sea ice covers about 24 percent of the Arctic Ocean whereas in 2007 the previous low was 29 percent. According to Walt Meier, a research scientist, "the Arctic is the earth's air-conditioner.." and we are going to see larger climate effects because we continue to lose it. During the coming months the water will refreeze, but once the summer months return the ice will be thin and more prone to melting.
The sea ice has declined much faster than predicted in the United Nations report in 2007 and some scientists believe that the Arctic Ocean could be free of summer ice by 2020. Many think this rapid warming is due to human release of greenhouse gases and not surprisingly atmospheric patterns in the Northern Hemisphere have already altered leading to greater weather extremes in the U.S. and other countries. As the ice is melting, sea levels are rising and the darker ocean surface is able to trap more of the sun's heat which in turn melts more ice. The scientific community already realizes how serious this issue is, now the public needs to realize that the Arctic melting at this rate shows that we are running out of time by failing to limit our emissions.
http://www.nytimes.com/2012/09/20/science/earth/arctic-sea-ice-stops-melting-but-new-record-low-is-set.html?_r=1&hp
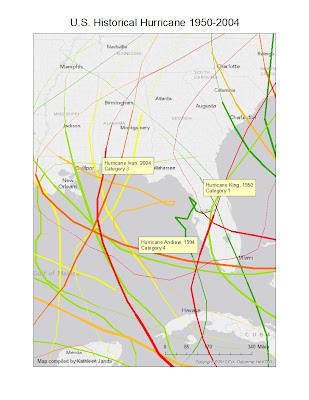
US Historical Hurricanes
Here is a map I made of Historical U.S. hurricanes from 1950-2004. The different colored lines represent different decades and the thickness in the colored line represents what category the hurricane was. I have labeled a few of the hurricanes in the map to show this. I am using the Engineering paradigm approach with this data which basically uses science and technology. In order to take a complexity based approach to this hazard I would need data on environmental change such as deforestation and climate change and the concentration of people in rural and urban areas.
Sunday, September 16, 2012
Landslides in Rudraprayag
http://www.dailypioneer.com/nation/95028-nine-more-die-in-fresh-landslides-in-cloudburst-hit-rudraprayag.html
http://india.nydailynews.com/newsarticle/5054a239b7445cb925000000/india-landslide-death-toll-jumps-to-45
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)